
You’ve spent countless hours meticulously planning and executing your woodworking project, only to have a poorly chosen router bit leave unsightly marks or ruin a delicate detail. Selecting the appropriate router bits is paramount for achieving professional-grade results, elevating your craftsmanship, and ensuring your hard work isn’t compromised. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the art of choosing the right router bits for various woodworking tasks.
Key Takeaways:
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Understand Bit Profiles | Different bit profiles serve distinct purposes, from straight cutting to intricate moldings. |
| Match Shank Sizes | Ensure compatibility between your router bits and the collet size of your router. |
| Consider Material | Some bits are better suited for specific wood types, like carbide for hardwoods. |
| Use Bearing/Template Guided Bits | These bits aid in consistent cuts and intricate designs, respectively. |
| Prioritize Safety | Sharp bits, proper feeding techniques, and protective gear are essential. |
Section 1: Understanding Router Bits – Anatomy and Functions
At their core, router bits consist of three main components: the shank that inserts into the router, the body that determines the cut’s depth and profile, and the cutting edge that removes material from the workpiece. However, the true magic lies in the diverse array of cutting profiles available, each tailored to specific woodworking applications.
Straight bits, for instance, are ideal for creating grooves, dados, rabbets, and mortises. On the other hand, round-over bits gracefully soften sharp edges, while edging bits impart decorative profiles. This visual guide illustrates the array of router bit profiles and their corresponding functions.
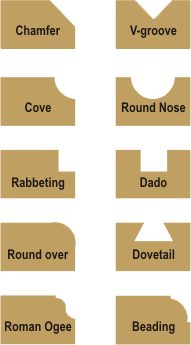
A variety of router bit profiles for different woodworking tasks.
Section 2: Matching Router Bits to Your Router
Before diving into router bit selection, ensure compatibility between the bits and your router. Specifically, the shank size of the bit must correspond to the collet size (the opening that grips the bit) on your router. Common shank sizes include 1/4-inch and 1/2-inch, with larger shanks providing greater stability and reduced vibration during operation.
While 1/4-inch shanks are suitable for lighter tasks, many woodworkers opt for 1/2-inch bits when working with hardwoods or more demanding applications. This simple yet crucial step prevents frustrating scenarios where a bit won’t securely mount in your router, potentially leading to hazardous situations. Consult your router’s manual for its recommended shank size.
Section 3: Selecting Router Bits for Common Woodworking Applications
With an understanding of bit anatomy and compatibility, let’s explore the ideal router bits for various woodworking applications:
- Straight Cutting: For creating grooves, dados, rabbets, and mortises, turn to straight bits. These versatile bits feature a cylindrical cutting edge that plunges straight into the material, offering precise control over the cut’s depth and width.
- Edge Forming: To soften sharp edges or add decorative flair, round-over and edging bits are your go-to tools. Round-over bits feature a radiused cutting edge that gently rounds over the corners, while edging bits impart intricate profiles like beading, reeding, or fluting.
- Joinery: For creating specific joint profiles, such as box joints or dovetails, specialized router bits are available. A dado bit, for instance, efficiently cuts flat-bottomed grooves for joining perpendicular pieces.
- Molding & Decorative Cuts: Elevate your projects with decorative moldings, coves, and intricate designs using molding and specialty bits. These bits enable you to reproduce classic architectural elements or create unique flourishes that set your pieces apart.
The following table summarizes common router bit profiles and their corresponding applications:
| Router Bit Profile | Woodworking Application | Example Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Straight | Grooves, dados, rabbets, mortises | Cabinets, shelving units, box joints |
| Round-Over | Softening edges | Tabletops, furniture, picture frames |
| Edging | Decorative edge profiles | Moldings, trims, baseboards |
| Dado | Flat-bottomed grooves for joining | Box joints, shelving units |
| Molding | Architectural moldings, coves | Crown moldings, chair rails, mantles |
Section 4: Additional Considerations When Choosing Router Bits
While the intended application and your router’s compatibility are primary factors, several additional considerations can optimize your router bit selection:
- Material Compatibility: Different wood types and densities may require specialized bits. For example, carbide-tipped bits are better suited for hardwoods due to their durability and resistance to wear.
- Bearing Guided vs. Template Guided: Bearing-guided bits feature a small bearing that rides along the workpiece, ensuring consistent cuts and preventing tear-out. Template-guided bits, on the other hand, follow a pre-made template for intricate or repetitive designs.
- Number of Flutes: The cutting edges of router bits are called flutes. More flutes generally result in faster cutting and improved chip removal, but fewer flutes may be preferable for certain materials or applications.
- Safety Precautions: Always prioritize safety when working with router bits. Use sharp, well-maintained bits, employ proper feeding techniques (feed against the bit’s rotation), and wear eye protection to safeguard against flying debris.
By considering these additional factors, you can further refine your router bit selection, optimizing performance, longevity, and safety in the workshop.
Call to Action
Now that you’re equipped with the knowledge to choose the right router bits, why not put it into practice? Explore our extensive selection of high-quality router bits and take your woodworking projects to new heights. Don’t hesitate to share your favorite router bit types or ask questions about specific applications in the comments below.
FAQs
What is the difference between a straight bit and a spiral bit?
A straight bit has a cylindrical cutting edge that plunges straight into the material, while a spiral bit features a twisted or helical cutting edge. Spiral bits are better suited for plunging cuts or creating deep grooves and mortises as they efficiently remove waste material and prevent clogging.
Can I use the same router bit for different materials?
While some router bits are versatile enough for multiple materials, it’s generally recommended to use material-specific bits for optimal results. For instance, carbide-tipped bits are better suited for hardwoods, while high-speed steel bits may suffice for softwoods. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for material compatibility.
How do I determine the correct feed rate when using a router bit?
The ideal feed rate depends on several factors, including the bit size, material type, and router speed. As a general rule, smaller bits require slower feed rates to prevent burning or tearout, while larger bits can handle faster feed rates. It’s always better to err on the side of caution and adjust your feed rate based on the results.
How do I ensure my router bit cuts are clean and tear-out free?
Several techniques can help achieve clean, tear-out free cuts with router bits:
- Use sharp, well-maintained bits.
- Employ a backing board or sacrificial surface to prevent tear-out on the exit side.
- Adjust your feed rate and router speed based on the material and bit size.
- Use a climb cut (feeding the workpiece against the rotation) for the final pass.
- Consider using a bearing-guided bit for added control and consistency.
Can I use larger router bits for more stability?
Yes, using larger shank sizes (typically 1/2-inch) can provide greater stability and reduce vibration during operation, especially when working with larger bit diameters or denser materials. However, ensure your router is designed to accommodate larger shanks and adjust your feed rate accordingly.
How do I safely change router bits?
Always unplug your router before changing bits to prevent accidental startups. Use the appropriate wrenches or collet nut to securely tighten the bit in place, ensuring it’s properly seated and free of debris. Never make adjustments or changes while the router is running.
How can I extend the life of my router bits?
To maximize the lifespan of your router bits, follow these tips:
- Use the appropriate bit for the material and application.
- Avoid overheating or burning the bit by adjusting your feed rate and router speed.
- Store bits properly to prevent damage or dulling.
- Regularly sharpen or replace dull bits.
- Clean and maintain your bits according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
External Resources
For further exploration of router bits and woodworking techniques, check out these helpful resources:
- Essential Router Bits for Woodworkers (External Link)
- Router Bit Buyers Guide (External Link)
- (YouTube Video)

